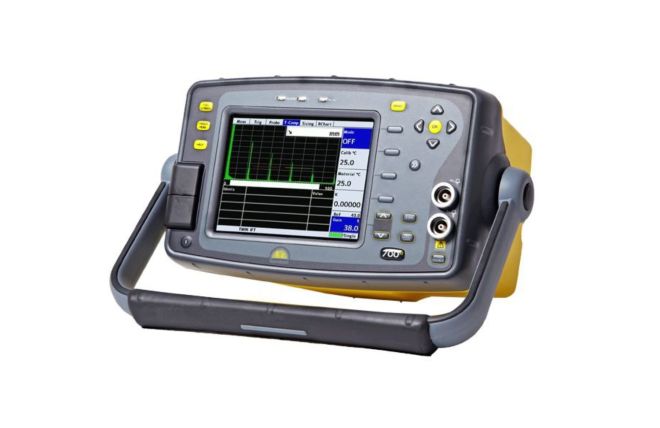
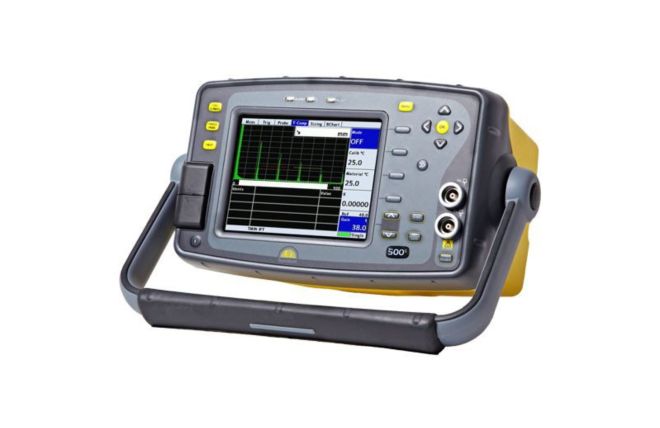
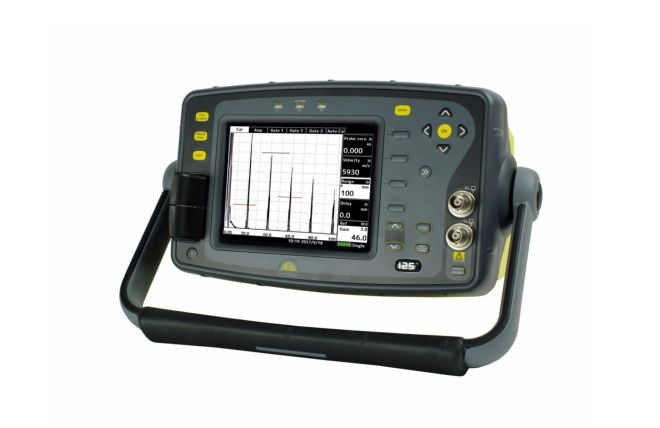
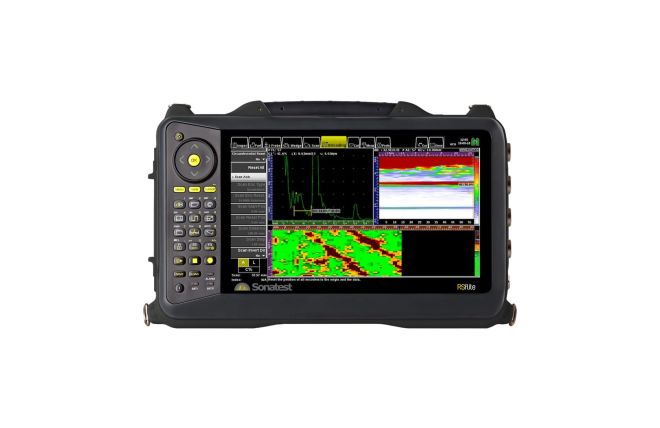
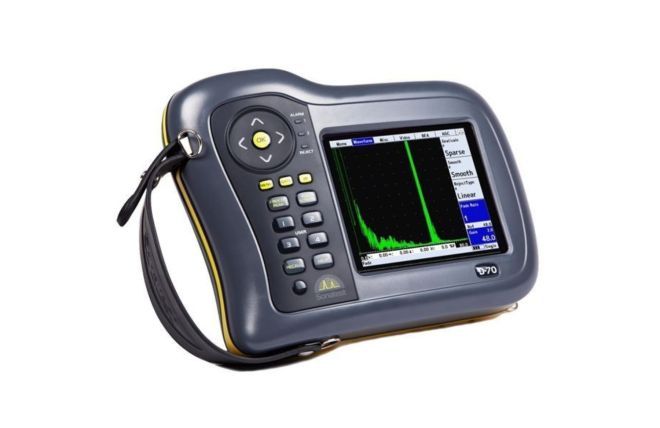
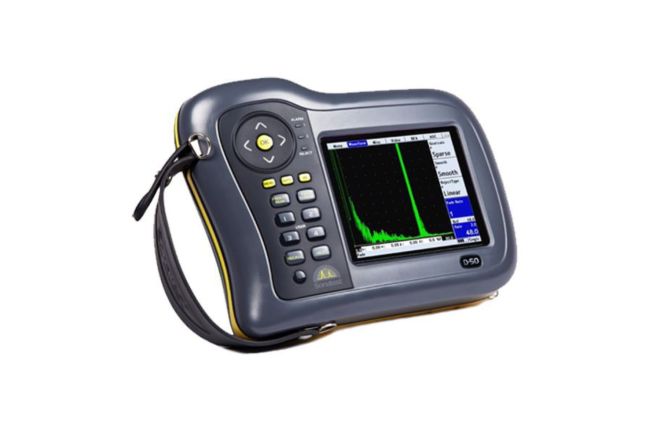
Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors
Our comprehensive range of portable ultrasonic flaw detectors provide the user with unrivalled flexibility and performance in the field of Non-Destructive Flaw detection.
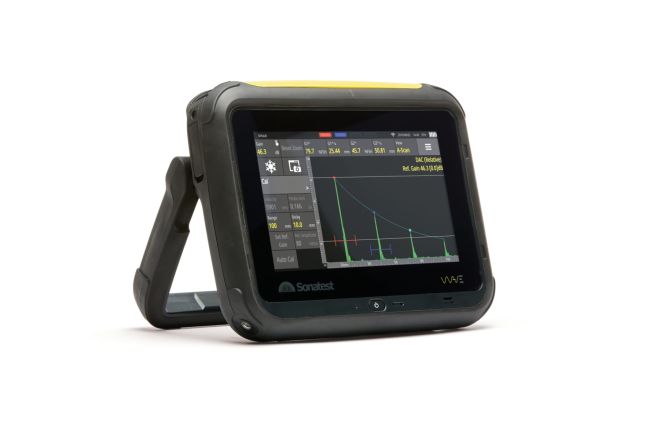

Robust and User-Focused Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors
Manufactured by Sonatest, our collection of ultrasonic flaw detectors is built to be robust and durable. With the needs of the end-user at the heart of their design, these detectors reliably deliver accurate and reliable results. They play a crucial role in ensuring safety and material integrity across various industries, including aerospace, oil and gas, and manufacturing.
Flexible Testing Systems with Field Upgradeability
A remarkable feature of our flaw detectors is their field upgradeability. You can perform updates and add new capabilities on-site, reducing downtime and enhancing operational flexibility. This versatility makes our flaw detectors essential and user-friendly tools for a wide range of non-destructive testing (NDT) applications.
Portable Ultrasonic Flaw Detection for Fieldwork
Our range of portable ultrasonic flaw detectors is designed for ease of use and mobility, being lightweight and compact. This high portability, combined with exceptional performance, makes them perfect for on-site inspections and fieldwork. Technicians can conduct reliable non-destructive testing wherever needed, enhancing efficiency and flexibility.