Rail Sector
The rail industry has been transporting people and goods around the world since the 19th century. The public's safety using the network and those living near lines and stations is paramount.
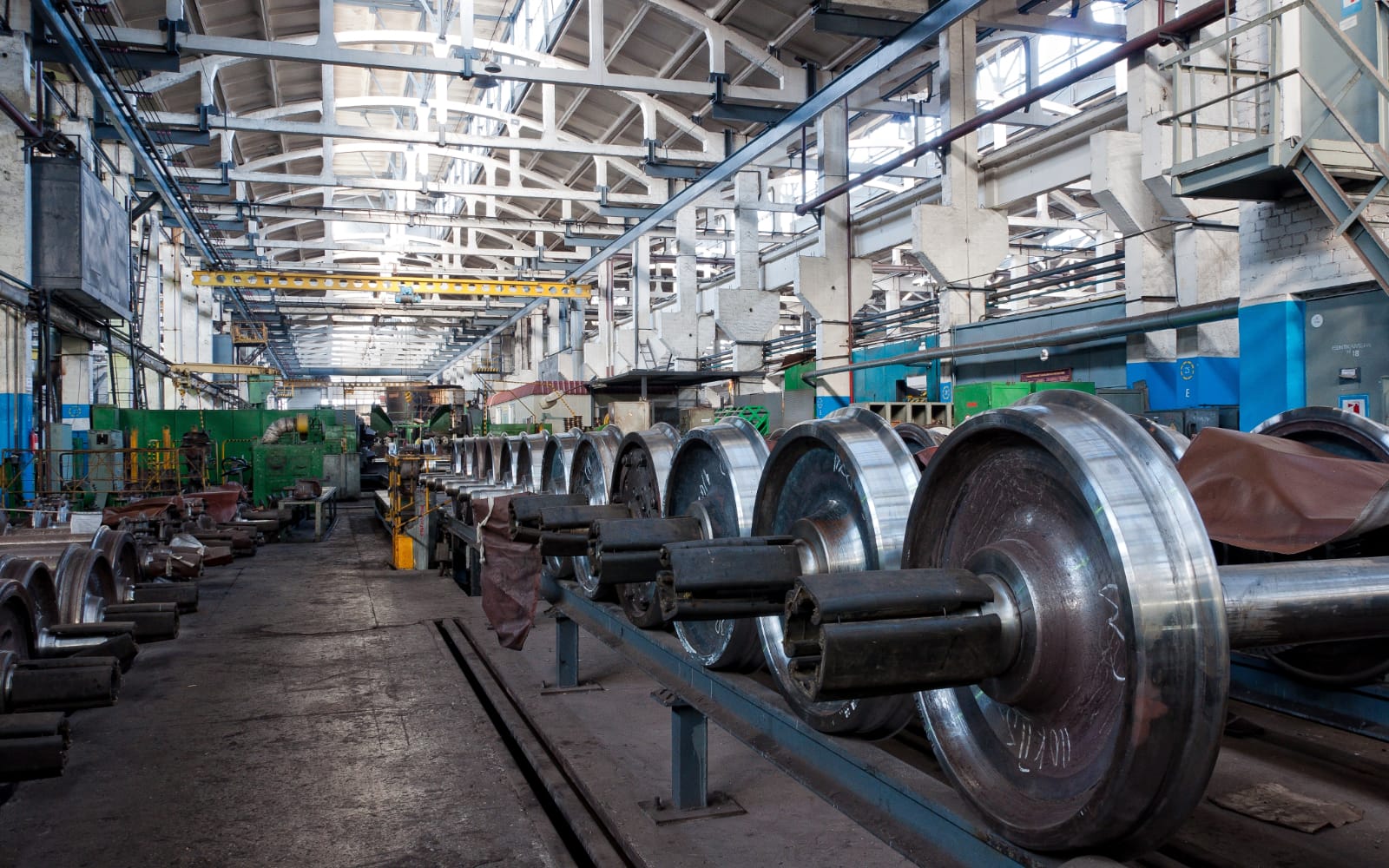
Non-destructive Testing (NDT) is a key part of the safety culture in the industry, with inspections being carried out on everything from the rails, axels, steam engines, rail bridge infrastructure etc., to ensure the continuing safe operation of our rail networks.

Ultrasonic inspection methods can be found in all aspects of rail manufacture and in-service testing. Regular inspections of the rail lines highlight cracking and corrosion. The rail axles and wheels are routinely inspected to ensure there are no defects from the manufacturer or service that may lead to failure.
1. Inspection Targets
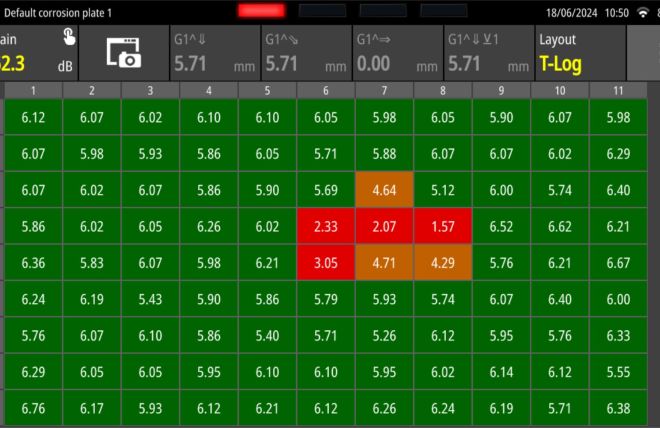
- Rail line: Rail lines are inspected for corrosion and cracking in critical areas; these are mainly in-situ inspections requiring access to the line.
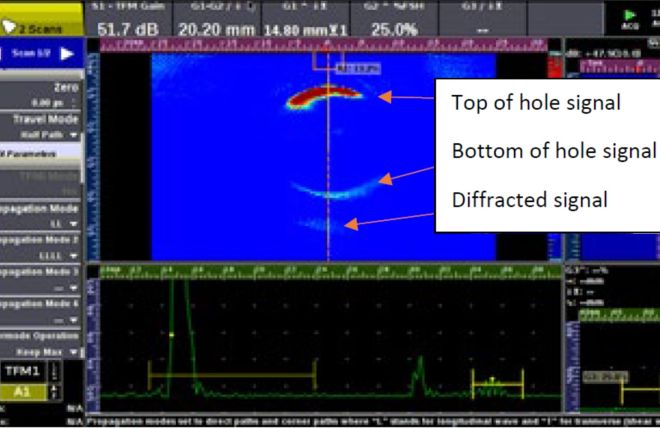
- Train Axels and wheels: Axel and wheel inspection is carried out at manufacture, and periodically during service life; the inspector is looking for cracking or mechanical damage.
- Cabin Structural welds: Modern train cabins are constructed from welded aluminium; critical welds and plate thicknesses are inspected to ensure compliance with standards.
2. Challenges
- Access to rail lines: Access to rail sections is often only available at night or low traffic times to ensure safety for workers.
- Access to axels in service: Inspection of rail axels requires access to certain test surfaces; this may need full removal from the train and inspection in a workshop.
- The complex geometry of axles: Axels can have complex geometries depending on the attachments; this requires highly skilled inspectors to carry out the inspections.
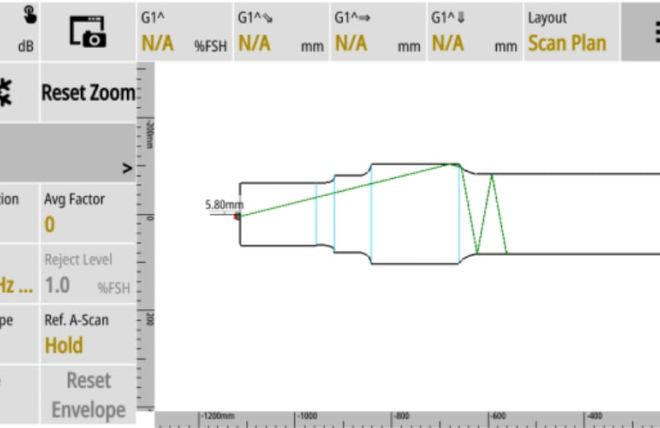
Sonatest offers a range of ultrasonic inspection solutions for the rail industry; the Railscan 125+ is specifically designed for rail inspection and has improved on the industry feedback and requirements from the previous Railscan generations. The Wave introduced the live scan plan with CAD file downloads allowing for axle and rail profiles to be viewed live and any possible defect signal to be plotted accurately.
Phased array inspection is a growing method in the rail industry, with more and more applications being found where this advanced technology can be used. The VEO3 comes with all the capabilities and power needed to carry out scanning of any project in the rail industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ultrasonic testing in the rail sector is critical for ensuring the safety and reliability of rail infrastructure and rolling stock. This method helps in detecting internal defects such as cracking or corrosion in rails, axles, and wheels that could potentially lead to failures if not identified and managed appropriately. Ultrasonic inspection is also used in the construction of the coach, welds, and critical components to ensure passenger safety.
The design of railroad components is theoretically made for an infinite lifetime base on fatigue stress, but the actual load demand in real-world can damage rail, wheel, axle, and all other components. Inspection frequency varies based on component usage and regulatory standards but generally includes routine checks at specified intervals. Rails are often examined during scheduled maintenance stops, while critical components like axles and wheels are inspected both post-manufacture and at routine service intervals to ensure safety throughout their operational life.
Sonatest utilises advanced ultrasonic testing technologies including the Railscan 125+ for specialised rail inspections, the Wave is used in both the axle and rail inspections utilising the CAD import overlay to help inspections of complex geometry parts, and the VEO3 device, equipped for phased array inspections. These technologies allow for detailed and accurate assessments enabling inspectors to identify imperfections and ensure compliance with standardised inspections.
Rails are designed to be strong and stable for different speeds and loads. The variety of sizes, shapes, joints, and welds makes many inspection scenarios to be unique. The wear of the track changes its shape, and the location of the defect is not always clear. Sometimes, several methods must be conducted to achieve a full coverage and characterisation. Additionally, Key challenges include restricted access to certain parts of the rail infrastructure, especially during peak operational hours which may necessitate night-time inspections.