- Application Notes
Spot-Weld Ultrasonic Inspection
Spot-welds on automotive components and other structures require post weld and in service inspection for a number of possible failure modes including insufficient fusion area, offset bonding of layers, cracks etc.
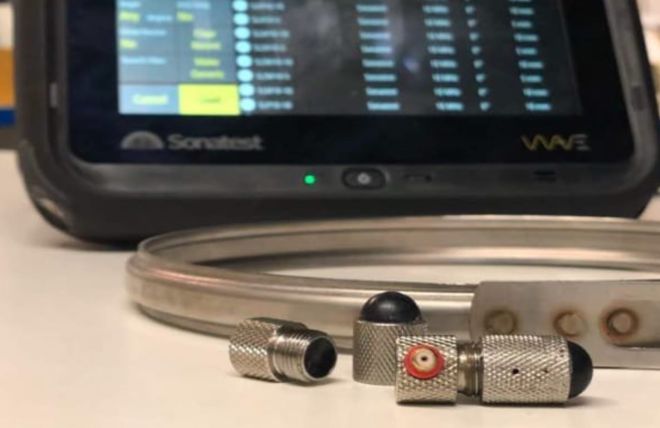
Sonatest rubber tips are designed to be used with the RDT delay line family and offer an effective alternative to the more traditional approach of water filled contact probes.
They have better life expectancy than water filled tips and the use of rubber dramatically reduces the amount of couplant required to ensure good contact. The flexible nature of the rubber ball works exceptionally well on uneven surfaces.

Fig. 1 - Spot weld transducers and rubber ball tips
The inspection method utilises known signal responses from a "good" weld as a baseline for following inspections, the amplitude and location of signals can identify defective welds (see Figures 2 – 5 for example scans).
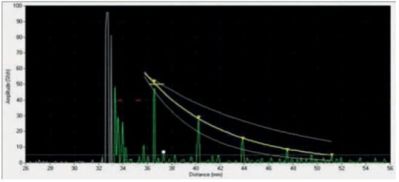
1. Good weld
With a good spot weld, the amplitudes of the subsequent echoes drop relatively quickly because the weld structure is coarse grained and therefore has a high sound attenuation characteristic. The echo intervals correspond to the total thickness of the welded sheets.
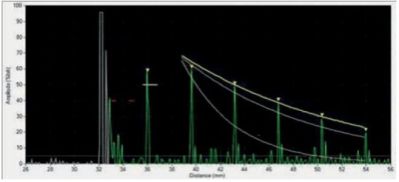
2. Adhesive / Loose / Stick weld
If there is an adhesive weld (also called a cold shot or a stick weld), then an extended echo sequence is received from the two sheets. In the case of a cold shot, however the grain structure is different (fine grained) and this leads to a long echo sequence due to reduced sound attenuation.
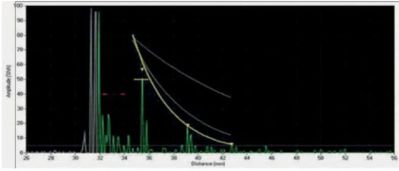
3. Burnt weld
If a burnt weld condition is present then the weld material is highly attenuative due to the coarser grain structure is possesses. This leads to the transmitted ultrasound dropping off rapidly because of the higher attenuation, as shown above with the reduction in echoes received and amplitude.
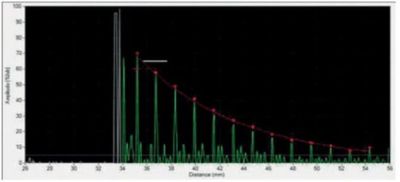
4. Non-fused / Loose plate
A non-fused/loose weld leads to a long echo sequence with short echo intervals corresponding to the single (upper) plate thickness only.
Conclusion
Manual testing can be very effective in detecting ‘defective’ weld conditions associated with spot weld joining process. This is always operator dependant and needs a good basic understanding of ultrasonic principles. The main benefit of manual testing is primarily the low cost and portability when compared to larger fixed or robotic systems.
Recommended Tool Package
| Category | Part# | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Unit | WAVE / D70 digital flaw detectors | |
| Probe | RB210 10MHz single crystal transducer, used with 10mm spot weld ball delay line – codes 151631 / 151635 |
Please contact our Applications Team if you have any questions. You can also find more solutions on our website.
Stay up to date with our latest content. Sign up here to get our blogs delivered straight to your inbox.
Filter by Industry
- Aerospace Aeronautical
- Aerospace Astronautical
- Chemical & Petrochemical
- Oil & Gas
- Nuclear Energy
- Wind Power Renewables
- Transport Network Infrastructure
- Rail
- Military
- Maritime Shipping
- Automotive
- Pharmaceutical
- Mining
- Construction & Infrastructure
- Technology & Research
- NDT Service Providers
- NDT Education