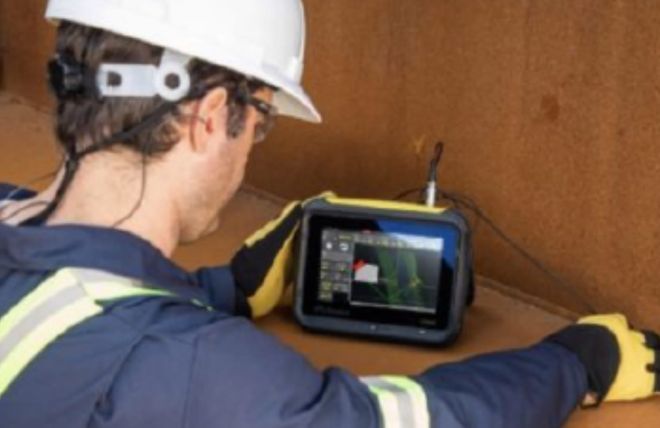
- Application Notes
Inspection of a Welded T-joint
A T-joint consists of two plates welded at 90° to each other in the form of a 'T'. Commonly used in the structural industry, T- joints generally use fillet or groove type welds on each side of the vertical plate, these welds can be ‘part’ or ‘full’ penetration welds, each presenting their own challenges.
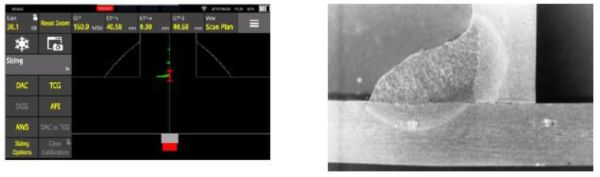
Fig. 1 - WAVE scan plan (left) for detection of the unfused land in a T-Joint as highlighted (right)
Lamellar Tearing
Lamellar tearing occurs when there is a weld contraction combined with low ductility of the base metal. This generates a very high stress concentration, located in the base metal, outside or close of the heat affected zone (HAZ). The tearing is generally parallel to the weld fusion surface.
Unfortunately, T-joints as well as corner joints are susceptible to this type of defect due to high through thickness strain.
Lamellar tearing can be easily detected by an inspection from the lateral web of the joint because of its predictable orientation (see Fig. 2).
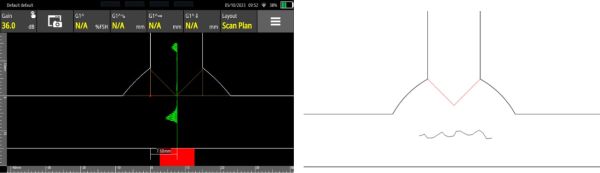
Fig. 2 - WAVE detection of lamellar tearing (left) and diagram showing the location of lamellar tearing in a T-Joint (right)
Cracking
A crack is a combination of metallurgical and mechanical failures. It usually occurs due to pre existing stresses, generally caused by thermal expansion, solidification, shrinkage or both. For example, aluminium alloys have a high thermal expansion coefficient and solidification shrinkage.
On a T-Joint with fillet welds on both sides, the second side is more restrained mechanically. Hence, this side will be more susceptible to cracks (as seen in Fig. 3).
It is difficult to correctly predict the orientation of cracks, as they can be detected from many inspection angles based on the sample geometrical aspects.
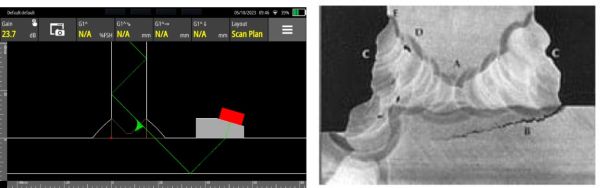
Fig. 3 - Toe crack detection on the WAVE (left) and an example of toe cracking of a T-Joint (right)
CODES & STANDARDS
Welded structures have to meet applicable codes and standards related to their intended use. The welding process, inspection technique and acceptance criteria vary.
For structural welding inspection to the American Welding Standard (AWS), the most important measurements are the indication level, reference level, attenuation factor and the indication rating. The Sonatest Wave has a built-in single touch application for inspecting to AWS requirements. Hence, after an AWS calibration, the user is able to select the AWS measurements associated with the corresponding gate. In addition, the indication rating is automatically calculated, which improves the reporting efficiency.
Recommended Tool Package
| Category | Part# | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition Unit | WAVE digital flaw detector | |
| Probe | Shear and transvers wave transducers available for any material and thickness requirements | |
| Software | Sonatest Companion Software |
Please contact our Applications Team if you have any questions. You can also find more solutions on our website.
Stay up to date with our latest content. Sign up here to get our blogs delivered straight to your inbox.
Due to the complex geometry of the part, in an A-Scan only view, signals can be difficult to interpret. small inaccuracies in probe positioning or the angle of reflection may place a signal as a defect in the weld when in fact it is it is a reflection from the internal wall. situations like this can lead to false calls and unnecessary repairs.
By utilizing the WAVE's unique scan plan and live ray tracing ability, the inspector is able to see exactly where a signal is positioned and give the inspector greater confidence in their result. the ability to screenshot the scan plan also enables more detailed reporting, giving clear and precise images of where any defect indication is positioned within the weld area.
This unique feature makes Wave an ideal instrument for T-joint inspection.
Typical Defects in T-joints
The most common defects in T-joint welds are cracks, lack of fusion and lamellar tearing all of which can be inspected with conventional ultrasonic methods.
Lack of fusion or Penetration
A lack of fusion occurs when the base metal is not melted during welding, resulting in a lack of cohesion. For T-joints, in a "part penetration|" weld there is an area of intentional lack of fusion between the two plates, in “full penetration” welds this area should be fused. This area is inspected to detect and lack of fusion in full penetration welds and measure the size of the unfused area in part penetration welds. The optimal way to detect such defects is utilising a straight beam configuration on the lower flange of the joint. However, this may not always be accessible.
Filter by Industry
- Aerospace Aeronautical
- Aerospace Astronautical
- Chemical & Petrochemical
- Oil & Gas
- Nuclear Energy
- Wind Power Renewables
- Transport Network Infrastructure
- Rail
- Military
- Maritime Shipping
- Automotive
- Pharmaceutical
- Mining
- Construction & Infrastructure
- Technology & Research
- NDT Service Providers
- NDT Education


